Introduction
Automated driving is becoming increasingly relevant in research, industry, and society. Alongside technological development, questions concerning ethical decision-making and user acceptance are gaining importance.
The bachelor thesis by Lea Merz examines which ethical factors influence the user acceptance of automated driving systems and how these factors can be connected to an established technology acceptance model.
Background: Acceptance Models and the Research Gap
The Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) by Venkatesh et al. (2003) is a widely used model for explaining technology adoption, focusing on performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence, and facilitating conditions.
However, research on automated driving has shown that these components alone are not sufficient, as automated vehicles operate in safety-critical situations and must make ethically sensitive decisions. Ethical dimensions such as transparency, responsibility, fairness, and user autonomy have therefore become increasingly relevant. Despite that they remain largely overlooked in existing acceptance research, which tends to emphasize functional and technical system characteristics.
To address this gap, the bachelor thesis integrates ethical aspects into the UTAUT framework and examines their relevance for user acceptance in the context of automated driving.
Methodology
To investigate which ethical factors shape acceptance, the thesis uses a qualitative research design based on nine expert interviews. The experts come from fields such as automated driving, ethics, mobility research, and technology acceptance.
The material was analyzed using structured qualitative content analysis, leading to a systematic categorization of ethically relevant elements that influence acceptance.
Key Ethical Factors Identified in the Study
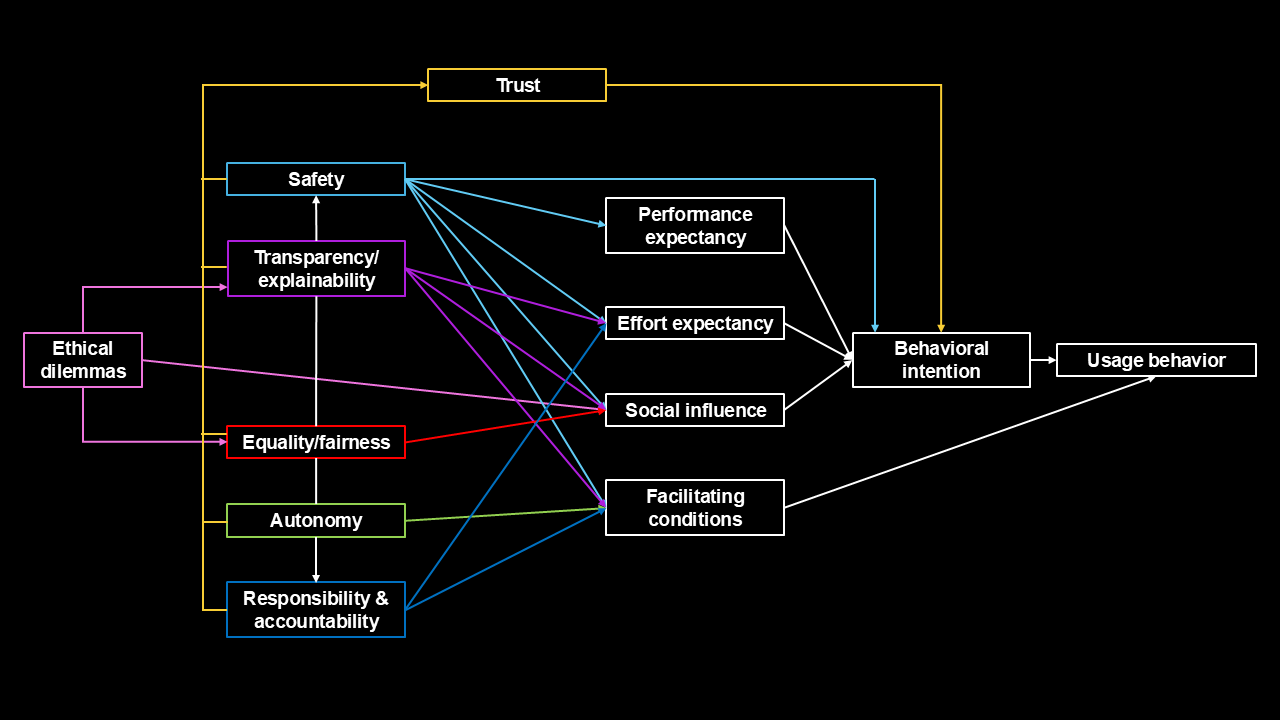
The results of the content analysis highlight several key categories:
- Safety
Safety emerged as a central theme, including physical safety, subjective perceptions of safety, system reliability, the protection of human life, and the system’s ability to adapt traffic-appropriate and socially confirming. These elements reflect both technical safety requirements and users’ personal feelings of security during automated driving.
- Autonomy
Autonomy refers to the user’s ability to maintain control, intervene when necessary, and voluntarily decide when to use automated driving functions. The category also captures the importance of allowing users to choose the degree of automation according to their individual preferences and comfort levels.
- Responsibility and Liability
The category of responsibility and liability addresses questions about accountability in the case of system malfunctions and responsibility for accidents involving automated vehicles. It includes issues such as the distribution of responsibility between users, manufacturers, and system developers, and the clarity of responsibility assignments in safety-critical scenarios.
- Transparency and Explainability
Transparency and explainability concern the availability of understandable information about system behavior, insight into system functions and limitations, and clarity regarding the decision-making processes of automated vehicles. These aspects relate to users’ need to comprehend how the system operates and what its functional boundaries are.
- Ethical Dilemmas and Decision Conflicts
This category describes system decisions in morally challenging situations, including situations in which collisions are unavoidable. It includes considerations about how automated vehicles should handle conflicting values and prioritize different outcomes in ethically sensitive traffic scenarios.
- Fairness and Equal Treatment
Fairness and equal treatment refer to the ethical requirement that automated vehicles avoid discriminatory behavior, consider different groups of road users equally, and prevent biases within system decision-making. These aspects highlight the importance of ensuring that automated systems act in a manner that is impartial and inclusive across diverse traffic situations.
- Trust
Trust emerges as a cross-cutting category influenced by perceived safety, transparency, and the degree of user control. It encompasses several elements, including confidence based on system experience, safe and predictable driving behavior, transparent communication between the vehicle and the user, and clarity regarding responsibility assignments.
Extension of the UTAUT Model
Based on the identified categories, the thesis develops an extended UTAUT model that incorporates ethically relevant factors into the existing acceptance framework. The model builds on the original UTAUT components and adds categories such as safety, autonomy, transparency, responsibility, fairness, and trust to more comprehensively reflect the specific characteristics of automated driving systems. This extension follows the theoretical structure of UTAUT and positions the ethical dimensions in relation to the empirical findings of the study.
Conclusion
The bachelor thesis by Lea Merz offers a structured presentation of ethical factors that influence the acceptance of automated driving systems.
By integrating theoretical concepts from the UTAUT framework and ethical research with qualitative expert insights, the study provides a clearer understanding of relevant user expectations in the context of automated mobility.
Future research should further examine the extended model, for example through quantitative approaches or structural equation modeling, in order to empirically validate the relationships between the identified ethical factors, trust, and user acceptance.
Reference
Venkatesh, N., Morris, M. G., Davis, N., & Davis, N. (2003). User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View. MIS Quarterly, 27(3), 425 478. https://doi.org/10.2307/30036540